What’s New!
The XSPOC 3.2 release expands on the artificial intelligence (AI)-driven autonomous control capabilities that were introduced in the 3.1 version, while also adding new features around uplift and economic opportunities for both rod- and gas-lifted wells. In addition, the 3.2 release debuts plunger lift trend analytics, which enables quick identification and trending for common plunger lift problems.
The latest version, XSPOC 3.2.2, offers all the above plus new capabilities for visual wellsite surveillance and chemical optimization.
See below for details on each of the key new features.
Be sure to check out our recorded webinar – XSPOC 3.2 – Introduction & Overview
Rod lift autonomous VSD setpoint optimization
You can now holistically optimize VSD setpoints using this new feature available in the Group Setpoint Optimization Control Center. Whether wells are suffering from poor runtime, under producing, or inconsistent speeds, this algorithm will optimize the VSD setpoints to ensure that the well is maximizing production and minimizing wear and tear on the equipment.
VSD setpoint optimization covers the following setpoints:
Pump Fillage, Setpoint Deadband, Speed Change, Stroke Delay, Start Up Speed, Speed Increase Size, Speed Decrease Size, Reference, Pump Fillage Setpoint, Secondary Pump Fillage Setpoint, Low Speed Time Setpoint, Slow Speed Time Setpoint, VSD Idling Enabled, Consecutive Pump off Strokes Allowed, Max Scaling, Min Scaling, Peak Speed, Low Speed, Max Speed, Min Speed
Gas lift autonomous injection rate setpoint optimization
Maximize drawdown and optimize production in gas lifted wells. This algorithm will analyze the injection rate’s effect on flowing bottomhole pressure for individual wells and iterate through several injection rate options to determine the rate that delivers the best production performance possible.
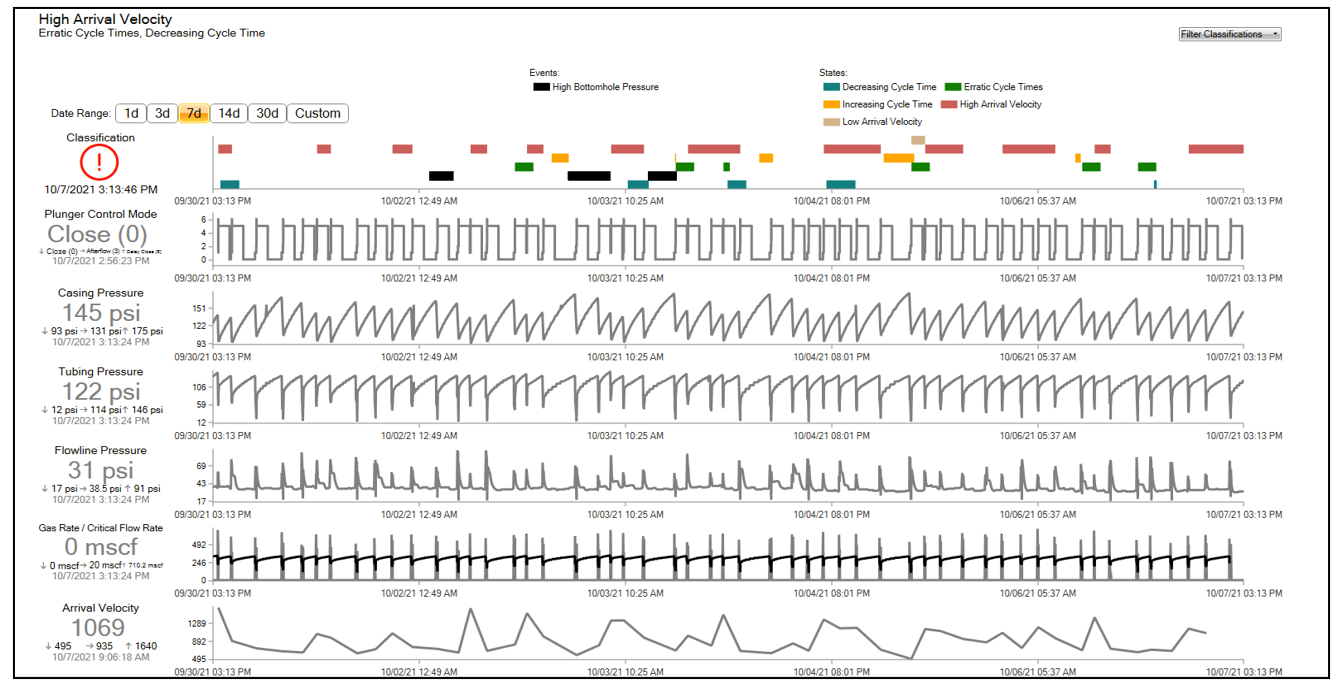
Plunger lift trend analytics
XSPOC can now provide sparkline trends for critical plunger lift analysis metrics, including lift modes, cycle times, and plunger velocity. Viewing this data in the software, you can standardize metrics across various plunger lift controllers in the field, enabling a holistic view of multiple wells’ performance. You can customize the operational dashboard to easily visualize critical conditions on all wells in a single screen, as well as track classifications for common problems such as erratic cycle times, backpressure anomalies, load factors, and irregular plunger velocity ranges. This is a powerful tool that can be used as a stand-alone technology, or be layered on top of existing SCADA platforms, so you can take advantage of trend analytics and longer-term performance measurements.
.
Rod pump uplift opportunity
You can now easily prioritize wells by uplift opportunity. Leveraging the predictive design intelligence from our RODSTAR™ design software, XSPOC can autonomously identify opportunities for production increase in wells running 24 hours with fluid levels above pump. The predictive logic determines the maximum speed for the unit to reach the well’s maximum capacity and allows users to quickly determine the highest priority wells for speed increases in under-producing wells
Gas lift economics
Determine the optimal injection rate in gas-lifted wells that are operating in a steady state. Utilizing the cost of separation or hydraulic horsepower, this algorithm helps users find the optimal injection rate for making the most money without liquid loading the well or over-injecting through the gas lift valve or orifice.
Well tree filtering
Filtering of the well tree nodes has been added so that branches will only display wells that meet this additional filter criteria. This significantly reduces the number of groups that need to be created. As an example, prior to this feature an admin would need to setup ‘Bad Communications’ sub-groups for every area or operator route. With filtering, a user can simply select the main area or route group, and then apply a ‘Bad Communications’ filter to display only those nodes — eliminating the need for all the subgroups. We have also added a ‘Recently Visited’ feature, so that recently visited nodes are available on a selectable list. This is very helpful when going back and forth between wells.
OPC-UA Support
XSPOC now supports OPC-UA, in addition to the legacy OPC-DA technology. OPC-UA offers much more robust security with improved authentication methods, and allows IP-based connectivity that gets away from the pain points of DCOM used by OPC-DA.
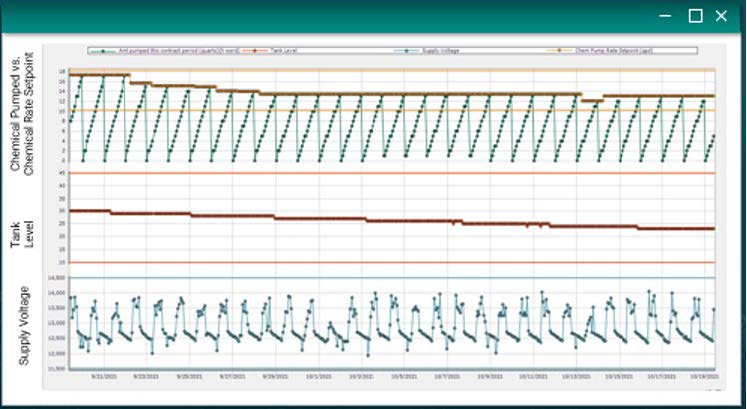
AUTONOMOUS CHEMICAL INJECTION OPTIMIZATION (XSPOC 3.2.2)
XSPOC’s new autonomous chemical injection optimization feature allows you to proportionally control your chemical injection to parameters already being tracked in the software, such as production, temperature, load, and more. For example, most wells in XSPOC are tracking production, either through frequent well tests or inferred production calculations. You can set up the software to proportionally adjust chemical injection rates based on the production rates, so that you are dosing the right amounts to avoid over-injecting and overspending, or even worse, under-injecting and risking asset integrity, flow assurance, or safety issues.
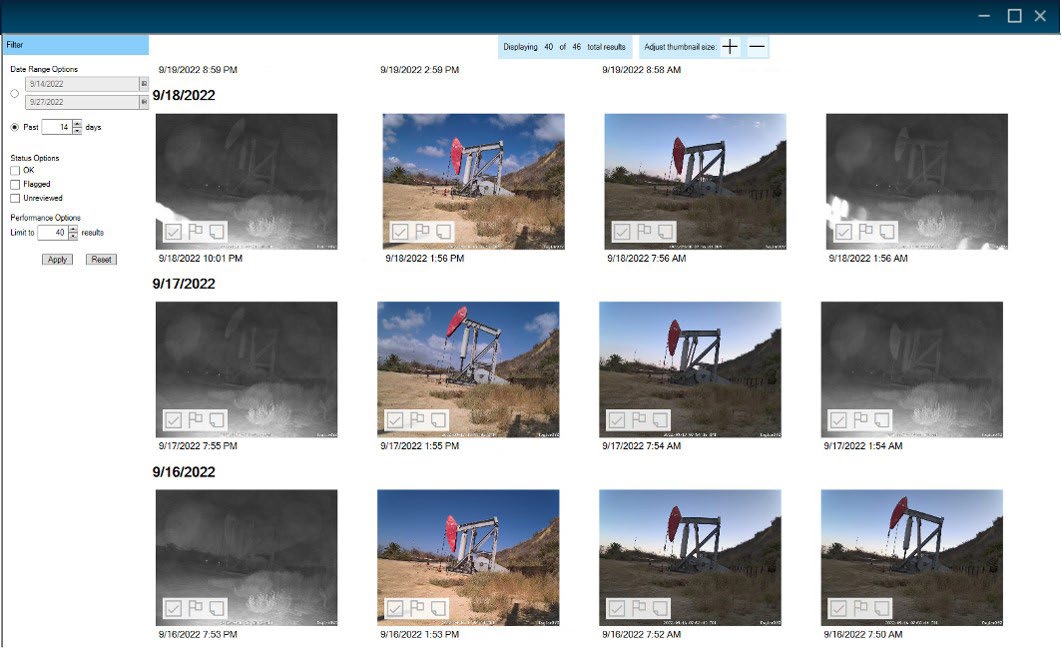
SNAPSHOT ADVANCED CLASSIFICATION PHOTO GALLERY (XSPOC 3.2.2)
XSPOC’s SnapShot photo gallery feature offers an advanced classification photo gallery with IP camera integration, allowing you to quickly detect problems – whether that’s a stuffing box leak or a bridle coming off a pumping unit – without driving to location. The gallery provides a holistic view of your photos all in one place, where you can review and classify the images as good (no issues detected), flag others that raise concerns, and add comments for additional details. You can choose how often you want the camera to take photos, as well as access on-demand photos for a live view of your wellsite.
Release Notes
Detailed XSPOC release notes, including additional new features, improvements, and bug fixes, can be found here.
Upgrade
Ready to upgrade? Click here to request an upgrade.